

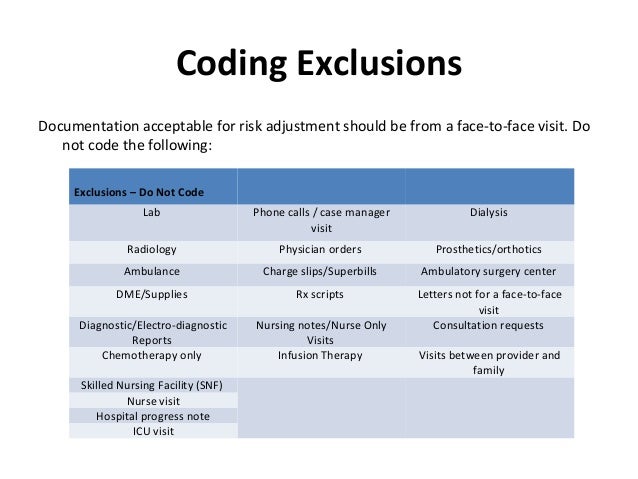
Using MEAT criteria ensures proper documentation for HCC diagnoses and even one element of each MEAT criteria documented satisfies the documentation required for an HCC diagnosis. Physicians can use the MEAT (Monitor Evaluate Assess and Treat) criteria when documenting HCC diagnoses. For HCC to be successful, the provider must report all diagnoses that impact the patient’s evaluation, care, and treatment including co-existing conditions, chronic conditions, and treatments rendered.
For example, major depression unspecified is not an HCC diagnosis but major depression, mild, single episode is an HCC diagnosis. Specificity in documentation is extremely important for HCC coding as it determines if the diagnosis is an HCC or not and also the category to which the diagnosis is assigned.
MEAT ABBREVIATION IN HCC CODING CODE
A patient’s risk adjustment factor (RAF) score is reset to zero every January 1, so it’s essential to document and code HCC diagnoses yearly to reflect accurate health status. Another essentiality of the risk adjustment model is the capturing of patients’ chronic conditions through documentation and coding every year. Ensuring an accurate problem list involves removing duplicative and inactive diagnoses and helps identify key areas for the assignment of HCC codes and RAF values.
MEAT ABBREVIATION IN HCC CODING FULL
EMRs have been full of data being put in by healthcare organizations for years, resulting in a lot of data, and most likely an inaccurate problem list. There are certain concepts to be followed for the HCC risk adjustment model, and having an accurate problem list is one of them. Reporting a complete picture of the risk adjustment factor increases the accuracy of the patient score and ideally reduces the need to request medical records or audit providers’ claims. According to the ‘American Academy of Family Physicians, “hierarchical condition category coding helps communicate patient complexity and paint a picture of the whole patient,” helping to appropriately measure quality and cost performance.

Healthy patients have a below-average RAF score so revenue from the insurance premium is transferred from healthy patients to patients with an above-average RAF score. The HCC model assigns a Risk Adjustment Factor (RAF) score to each patient basis patient’s demographics and diagnoses, which is a relative measure of how costly that patient is anticipated to be. This article walks through the basics of the risk adjustment model and how the provider can ensure accuracy in documentation and HCC coding to achieve swift and maximal reimbursements. With the rising number of beneficiaries enrolled in Health insurance Advantage plans, it’s more important than ever for healthcare organizations to pay attention to this model and make sure physicians are coding diagnoses appropriately to ensure fair compensation. Inaccurate HCC coding not only affects the patients and payers but also has an impact on healthcare organizations’ reimbursement. The Hierarchical Condition Category (HCC) risk adjustment model is an integral element within the medical coding world.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
